Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementation is crucial for businesses seeking to streamline and integrate their operations. It involves deploying a comprehensive software system that manages various core functions, such as finance, human resources, supply chain and customer relationship management.
However, undertaking a Successful ERP implementation comes with its fair share of costs, which must be carefully managed to ensure a successful project. This article provides a complete guide on how to control ERP implementation costs.
The Key Components Affecting ERP Implementation Cost
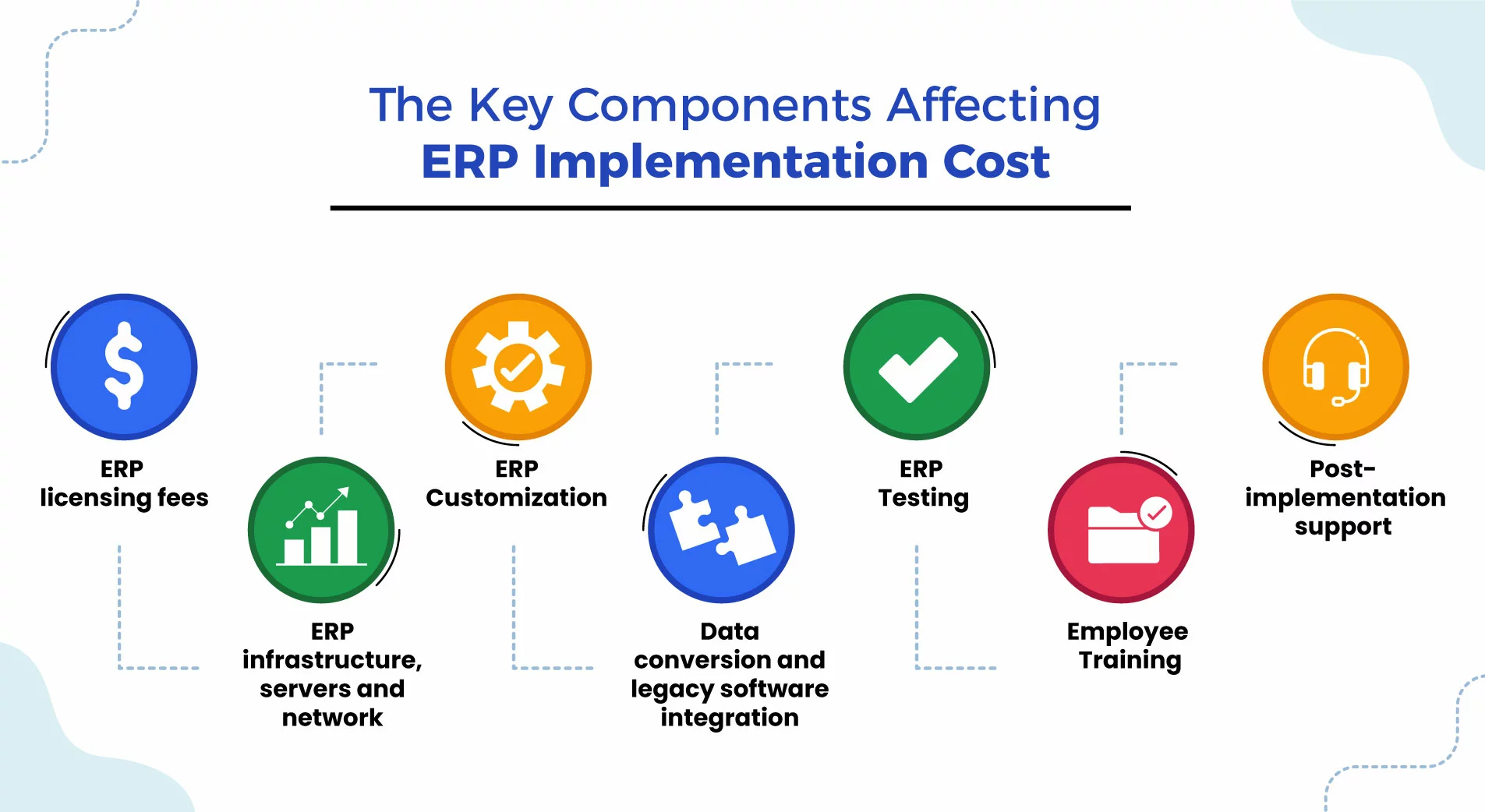
ERP software implementation entails various statutory and variable costs, which encompass licensing fees, infrastructure expenses, data conversion costs, custom development fees, testing expenses, third-party integration charges, training expenditures, and post-implementation support investments. Understanding these components is important to solid grasp the ERP implementation cost breakdown. Here below, we explain key cost components one by one.
1. ERP Licensing Fees
The first and foremost cost component that ERP clients need to bear initially is the licensing fee for the ERP software. Well, this cost varies from one software to another. Another factor affecting the cost is the number of users and your chosen software version. Some ERP software offers separate versions for small and medium businesses and large enterprises.
2. ERP Infrastructure, Servers And Network
Organizations need robust infrastructure, servers, and a reliable network to run an ERP system effectively. The costs include purchasing or upgrading hardware, ensuring sufficient server capacity and establishing a secure and efficient network infrastructure to support the ERP implementation.
3. Data Conversion And Legacy Software Integration
Integrating existing data from legacy systems into the new ERP solution is a critical and complex task. Data conversion costs involve extracting, cleaning and transforming data to fit the new system’s requirements. Additionally, integrating the ERP software with existing legacy applications or databases may require additional development efforts, leading to increased costs.
4. ERP Customization
Every organization has unique business processes and requirements. Customizing the ERP software to align with specific needs often incurs additional costs. Custom ERP Solution involves modifying or extending the ERP system’s functionality, user interfaces, workflows or reports to match the organization’s specific operational workflows and industry standards.
5. ERP Testing
Thorough testing ensures the ERP system functions correctly and meets the organization’s requirements. This includes activities such as system integration testing, performance testing and user acceptance testing. Costs associated with testing involve setting up test environments, acquiring testing tools and allocating resources for testing activities.
6. Employee Training
Proper training is vital for employees to utilize the new ERP system effectively. Costs related to employee training include developing training materials, conducting training sessions and providing ongoing support to address user queries and concerns. Investing in comprehensive training helps maximize user adoption and minimize errors during the implementation phase.
7. Post-Implementation Support
Last but not least, the cost component is the post-implementation support by the ERP vendor or the ERP implementation company. Post-implementation support costs include maintenance fees, help desk services, software updates, bug fixes, and vendor support contracts. Adequate post-implementation support is crucial to sustain the ERP system’s functionality and address any emerging issues promptly.
Risks Of Cutting Costs Too Much During An ERP Implementation
While it’s important to control average ERP implementation cost, cutting costs excessively can lead to several risks and challenges that may hinder the project’s success. Some of the risks associated with cutting costs too much during an ERP implementation include the following:
1. Inadequate System Functionality
The reduced budget allocation may limit the ability to customize or integrate the ERP system with legacy applications. This can result in an ERP solution that fails to meet critical business requirements or lacks necessary functionalities, diminishing the system’s effectiveness.
2. Data Integrity And Quality Issues
More investment in data conversion and data migration processes may lead to data integrity and quality problems. Only accurate or complete data can positively impact decision-making, operational efficiency and overall system performance.
3. Inadequate User Training
Another variable cost factor is the number of users and Insufficient training due to budget constraints can leave employees unfamiliar with the new ERP system. This may result in resistance to change, decreased user adoption and increased errors, diminishing the system’s overall value.
4. Increased Maintenance And Support Costs
Cutting post-implementation support and maintenance costs can result in inadequate support resources or limited access to software updates and bug fixes. This can lead to prolonged system downtime, increased disruption to operations and higher long-term maintenance costs.
5. Lack Of Scalability And Adaptability
Reducing the budget for infrastructure, servers, and network organizations may hinder the scalability and adaptability of the ERP system. This can limit the system’s ability to accommodate future growth, handle increased data volumes or integrate with emerging technologies.
6. Extended Implementation Timeline
More funding can delay the implementation timeline as organizations need help allocating resources effectively or addressing unforeseen challenges. Prolonged implementation periods can cause project fatigue, frustration and increased costs in the long run.
7. Overall Project Failure
Cutting costs excessively without considering critical project requirements and risks can ultimately lead to failure in ERP implementation. This can result in wasted time, effort and financial resources, negatively impacting the organization’s operational efficiency and competitiveness.
How To Reduce ERP Implementation Cost In A Right Way
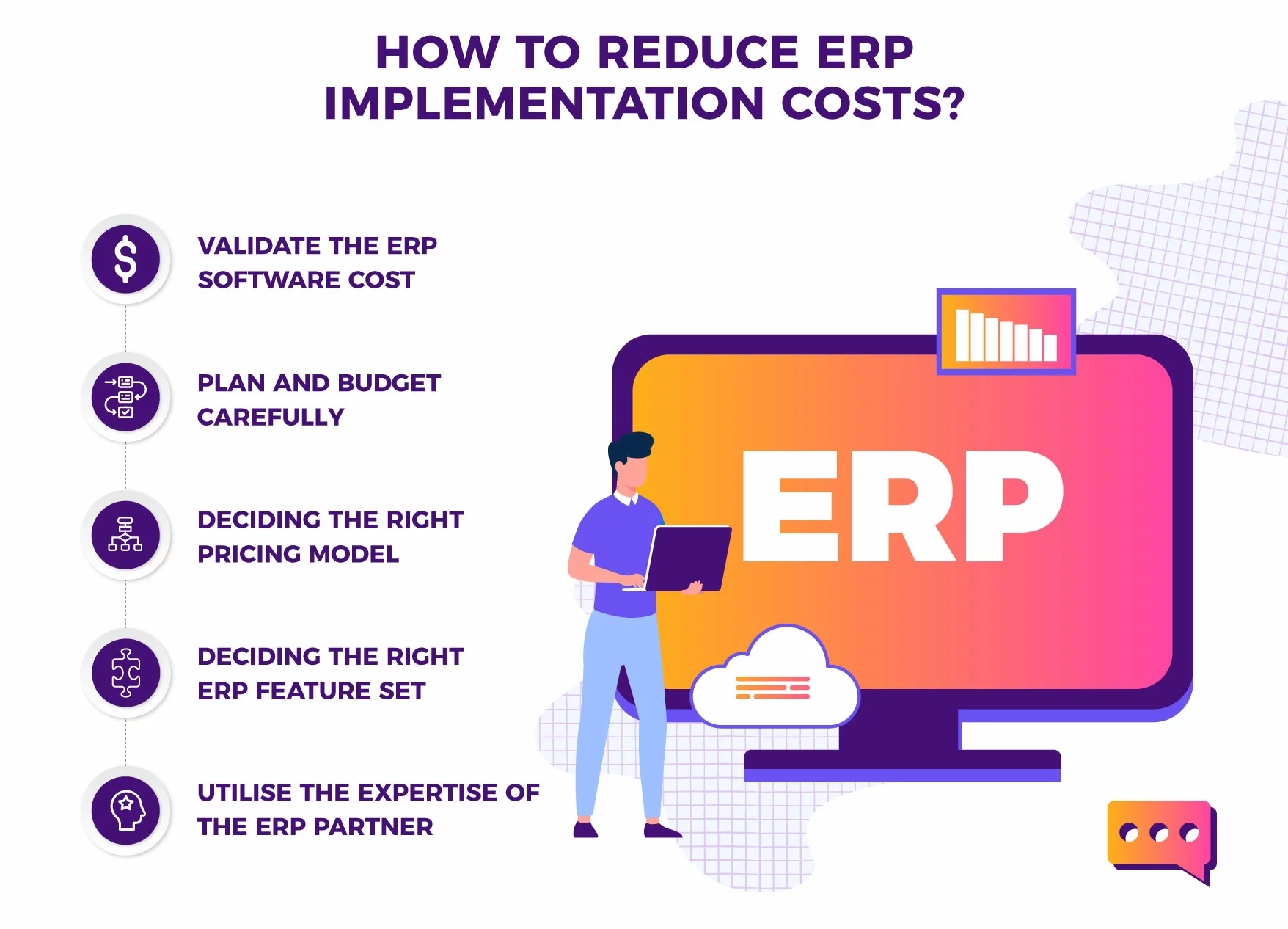
Reducing ERP implementation costs without compromising the project’s success requires careful planning, decision-making and leveraging the expertise of the ERP partner. Here are some strategies to reduce ERP implementation costs in the right way:
1. Validate The ERP Software Cost
Before committing to an ERP software solution:
1. Validate the cost and ensure it aligns with your budget and requirements.
2. Evaluate different vendors, compare their pricing structures and negotiate for favourable terms.
3. Consider the long-term total cost of ownership (TCO) which may include licensing fees, maintenance, upgrades and support.
2. Plan And Budget Carefully
Thorough planning and budgeting are crucial to controlling costs during an ERP implementation. Develop a comprehensive project plan, defining clear objectives, milestones and resource requirements. Conduct a detailed analysis of the ERP implementation phases, timeline and estimated costs. Anticipate potential risks and allocate contingency funds to mitigate unforeseen expenses.
3. Decide The Right Pricing Model
Choosing the appropriate pricing model for your ERP implementation can significantly impact costs. There are two primary pricing models to consider:
a. The On-Premise Model:
In this model, you purchase and host the ERP software on your own servers. While it may involve higher upfront costs for hardware, infrastructure and licenses, it provides greater control over the system and eliminates ongoing subscription fees.
b. Cloud-Based SaaS Model:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) ERP solutions are hosted in the cloud and accessed through a subscription-based model. While upfront costs may be lower, it involves ongoing subscription fees. Consider the SaaS model’s scalability, maintenance, security and flexibility benefits when evaluating its cost-effectiveness.
4. Decide The Right ERP Feature Set
Carefully evaluate the required ERP features based on your business needs. Avoid selecting excessive functionalities that may drive up costs unnecessarily. Focus on the core modules and functionalities that address your critical business processes. Customization and additional features can always be added later, reducing initial implementation costs.
5. Utilize The Expertise Of The ERP Partner
Engaging an experienced ERP partner can help reduce implementation costs by leveraging their expertise and best practices. They can provide valuable guidance in requirements gathering, process optimization, system configuration and user training. Partnering with an expert can help avoid costly mistakes, accelerate implementation and ensure the system is aligned with your business needs.
6. Leverage Prebuilt Templates And Configurations
Many ERP vendors offer prebuilt templates and configurations specific to industries or business functions. These templates can reduce implementation time and cost by leveraging preconfigured workflows, reports and integrations. These templates are often designed based on industry best practices, ensuring a streamlined implementation process.
7. Streamline Data Migration And Integration
Data migration and integration are critical and often complex aspects of ERP implementation. To reduce costs:
1. Carefully assess the necessity of migrating all historical data.
2. Focus on migrating only essential and current data to the new system, ensuring data accuracy and quality.
3. Simplify integration requirements by retiring or consolidating legacy systems no longer needed, minimizing integration complexity and costs.
8. Emphasize Training And Change Management
Investing in comprehensive training and change management programs can enhance user adoption and minimize errors, thereby reducing post-implementation costs. Prioritize end-user training to ensure proficiency in using the new ERP system. Implement change management strategies to address resistance and foster a positive attitude towards the new system, ensuring a smoother transition.
9. Continuous Improvement And Optimization
Once the ERP system is live, continuously monitor and optimize its performance and utilization. Regularly review and assess the system’s efficiency, identify areas for improvement and implement optimization measures. This proactive approach can lead to cost savings by eliminating inefficiencies, improving workflows and maximizing the ROI of the ERP investment.
How To Optimize ROI While Controlling ERP Implementation Costs?
Optimizing ROI (Return on Investment) while controlling ERP implementation costs requires a strategic approach focusing on maximizing benefits and minimizing expenses. Here are some key strategies to achieve this goal:
1. Clearly Define Business Objectives
Clearly define the business objectives and expected outcomes from the ERP implementation. This will help align the project with strategic goals and prioritize investments in areas with the most significant ROI.
2. Conduct A Cost-Benefit Analysis
Perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the potential returns and costs associated with the ERP implementation. Assess tangible and intangible benefits, such as increased productivity, reduced manual work, improved data accuracy and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
3. Prioritize Critical Business Processes
Focus on optimizing and automating critical business processes that greatly impact productivity, efficiency and customer satisfaction. By streamlining these processes, you can achieve significant cost savings and improvements in operational performance.
4. Embrace Best Practices
Leverage industry best practices and standards to optimize processes and workflows during the ERP implementation. Best practices often include standardized procedures that have proven effective, reducing the need for extensive customization and costly modifications.
5. Eliminate Redundant Systems
Identify and retire redundant legacy systems and applications that the new ERP solution can replace. Consolidating systems reduces maintenance and support costs while streamlining data integration and enhancing data accuracy.
6. Data Quality And Management
Ensure data accuracy and integrity throughout the implementation process. Implement data governance policies, cleansing procedures, and validation mechanisms to maintain high-quality data. Accurate data leads to better decision-making, improved operational efficiency and reduced costs associated with errors and rework.
7. Continuous Process Improvement
Implement a culture of continuous improvement after the ERP implementation. Encourage employees to provide their feedback and suggestions. This will lead to enhanced system functionality and optimization processes. Regularly review and refine workflows to identify efficiency gains and cost reduction opportunities.
8. Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define and track relevant KPIs to measure the effectiveness of the ERP implementation. Monitor productivity, cost savings, cycle times, inventory turnover, and customer satisfaction. Regularly assess KPIs to identify areas that require attention and implement corrective measures as needed.
9. Ongoing Training And Support
Provide ongoing training and support to users to maximize their proficiency and utilization of the ERP system. Well-trained employees are more efficient, make fewer errors and can uncover additional system capabilities that drive ROI. Ensure that support resources are readily available to promptly address user questions and concerns.
10. Vendor Relationship And Negotiation
Maintain a strong relationship with the ERP vendor and leverage it to negotiate favourable terms, such as discounted maintenance fees, extended support or free upgrades. Regularly assess vendor performance and explore opportunities to optimize costs without compromising quality.
11. Scalability And Future-proofing
Select an ERP solution that is scalable and capable of accommodating future growth and evolving business needs. Investing in a system that can adapt to changing requirements reduces the need for costly re-implementations or system replacements in the future.
Wrapping Up!
Most ERP implementation projects experience excessive spending primarily due to inadequate preparation and planning. The measures precisely address these concerns by emphasizing the importance of careful analysis and strategic planning.
You can achieve comprehensive control over costs for NetSuite Implementation Services by adhering to the measures above and following the tips while implementing a well-structured and detailed plan and roadmap.